Discover the essential steps to effectively repair composite bonding in this comprehensive guide.
Understanding Composite Bonding
Composite bonding is a dental procedure that involves applying a tooth-colored resin material to the teeth to improve their appearance. It is commonly used to repair chipped or cracked teeth, fill gaps between teeth, and reshape teeth. Understanding the basics of composite bonding can help you better navigate the repair process.
Composite bonding is a non-invasive procedure that can be completed in a single dental visit. It offers a more affordable and conservative alternative to other cosmetic treatments such as veneers or crowns. The composite material used in bonding is durable and can be color-matched to your natural teeth, providing a seamless and natural-looking result.
Common Issues with Composite Bonding
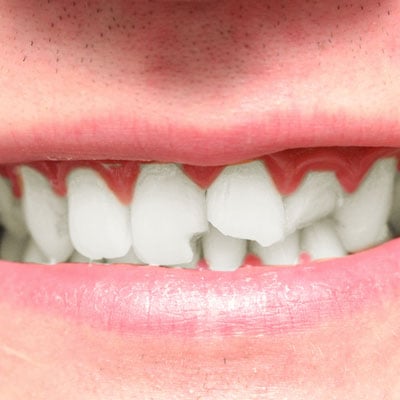
While composite bonding is a durable and long-lasting solution, it is not completely immune to damage or wear over time. Some common issues that may require repair include chipping, staining, or discoloration of the bonded area. Additionally, composite bonding may become rough or uneven due to normal wear and tear or improper bite alignment.
It is important to address these issues promptly to prevent further damage or complications. Repairing composite bonding can help restore the aesthetics and functionality of your teeth, ensuring a confident and beautiful smile.
Preparing for the Repair Process
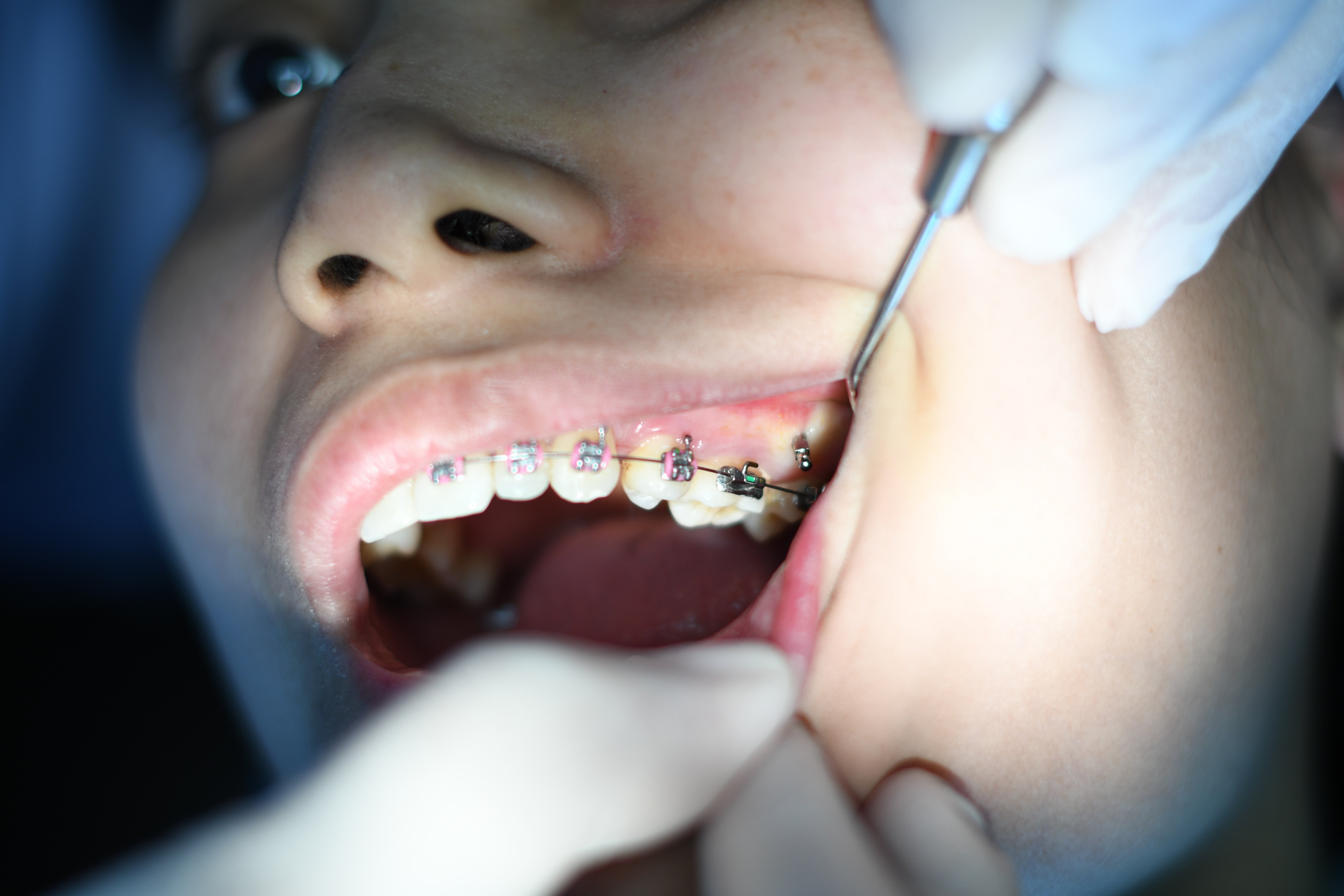
Before undergoing a composite bonding repair, it is essential to visit your dentist for an evaluation. Your dentist will examine the bonded area and determine the extent of the damage. They may recommend taking X-rays to assess the underlying tooth structure and ensure there are no additional issues.
Once the evaluation is complete, your dentist will discuss the repair options with you. This may involve removing the existing bonding material and applying a new layer, or simply repairing the damaged area. Your dentist will also take into consideration your preferences and expectations to achieve the desired outcome.
Step-by-Step Guide to Repairing Composite Bonding
Repairing composite bonding typically involves the following steps:
1. Preparation: Your dentist will clean the affected area and remove any existing bonding material.
2. Tooth Preparation: If necessary, your dentist will reshape the tooth or adjust the bite to ensure proper alignment.
3. Bonding Material Application: A new layer of composite resin will be applied to the tooth and shaped to match the natural tooth contours.
4. Bonding and Curing: The bonding material will be hardened using a special light to ensure a strong and durable bond.
5. Finishing Touches: The repaired composite bonding will be polished and smoothed to blend seamlessly with the surrounding teeth.
6. Bite Adjustment: Your dentist may make minor adjustments to your bite to ensure proper alignment and comfort.
By following these steps, your dentist can effectively repair your composite bonding and restore the appearance and functionality of your teeth.
Tips for Maintaining and Preventing Future Damage
After the repair process, it is important to take proper care of your composite bonding to maintain its longevity. Here are some tips to help you:
1. Practice good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent staining.
2. Avoid staining agents: Limit your consumption of foods and beverages that can stain the bonding material, such as coffee, tea, and red wine.
3. Quit smoking: Smoking can cause discoloration and damage to the bonding material. Quitting smoking can help preserve the appearance and durability of your composite bonding.
4. Wear a mouthguard: If you participate in contact sports or grind your teeth at night, wearing a mouthguard can protect your composite bonding from damage.
5. Regular dental visits: Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings. Your dentist can monitor the condition of your composite bonding and address any issues before they worsen.
By following these tips, you can prolong the lifespan of your composite bonding and minimize the need for future repairs.