Learn about the causes, prevention, and action to take against gum disease with this informative blog post.
Understanding the Basics of Gum Disease
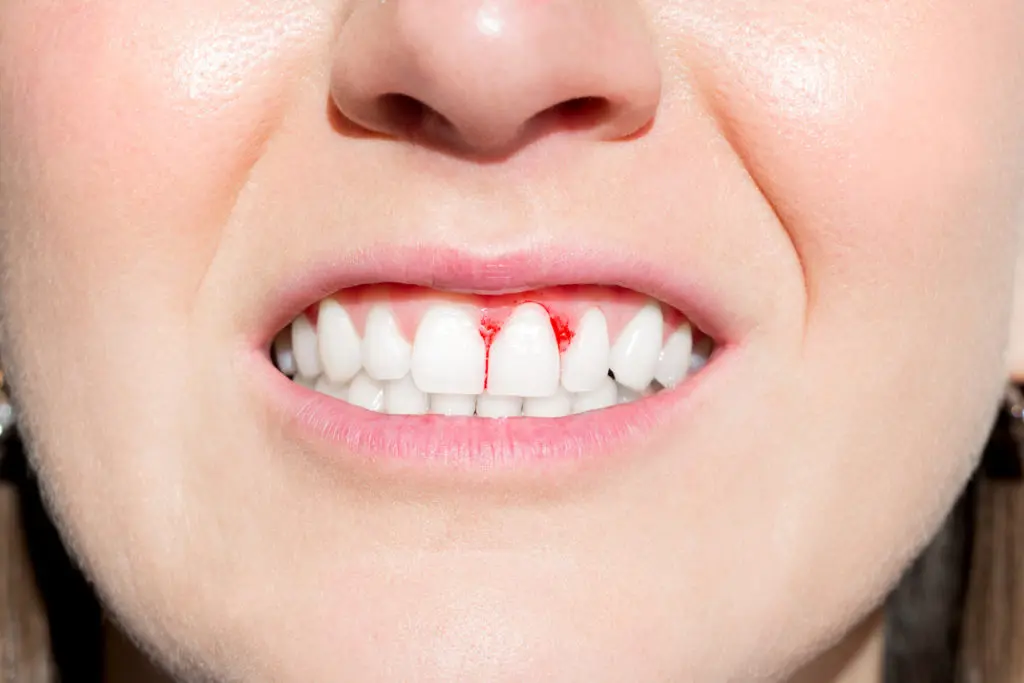
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other serious oral health problems.
There are two main types of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the milder form of gum disease and is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. Periodontitis is a more advanced stage of gum disease where the infection has spread to the supporting structures of the teeth, such as the bone and ligaments.
To prevent gum disease, it is important to understand the risk factors and take appropriate action. Regular dental check-ups, brushing and flossing daily, and avoiding tobacco products are some of the key steps in maintaining good oral hygiene and preventing gum disease.
In the next sections, we will explore the common causes of gum disease and the role of poor oral hygiene in its development.
Common Causes of Gum Disease
Poor oral hygiene is the most common cause of gum disease. When plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional. Tartar buildup irritates the gums and leads to inflammation and infection.
Other factors that contribute to gum disease include smoking, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menopause), certain medications, genetic predisposition, and underlying health conditions like diabetes.
It is important to be aware of these causes and take necessary steps to minimize the risk of developing gum disease.
The Role of Poor Oral Hygiene
Poor oral hygiene plays a significant role in the development and progression of gum disease. When plaque and tartar are not removed regularly, bacteria in the mouth can multiply and cause infection in the gums.
Brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash can help remove plaque and prevent gum disease. It is also important to visit your dentist regularly for professional cleaning and to address any oral health issues.
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices is essential in preventing gum disease and maintaining overall oral health.
Other Factors Contributing to Gum Disease
In addition to poor oral hygiene, there are other factors that can contribute to the development of gum disease.
Smoking and tobacco use are major risk factors for gum disease. Smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infection. It also reduces blood flow to the gums, impairing the healing process.
Hormonal changes can also make the gums more susceptible to gum disease. During pregnancy, hormonal fluctuations can cause an increased risk of gum inflammation and infection. Similarly, hormonal changes during menopause can also affect the health of the gums.
Certain medications, such as anticonvulsants and immunosuppressants, can also increase the risk of gum disease. These medications can affect the flow of saliva, which plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health.
Genetic predisposition can also make some individuals more susceptible to gum disease. If you have a family history of gum disease, it is important to be extra vigilant in maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking professional dental care.
Lastly, underlying health conditions like diabetes can increase the risk of gum disease. Diabetes affects the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels, which can impact the health of the gums and increase the risk of infection.
By understanding these factors, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent gum disease and maintain optimal oral health.
Preventing and Treating Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease starts with adopting good oral hygiene habits. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste, floss daily to remove plaque from between the teeth, and use an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria in the mouth.
Regular visits to the dentist are also crucial in preventing gum disease. Your dentist can perform professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar, as well as identify any early signs of gum disease. They can also provide guidance on maintaining good oral hygiene and offer treatments to address gum disease if necessary.
In some cases, more advanced treatments may be required to treat gum disease. These can include scaling and root planing, gum surgery, and antibiotic therapy.
Taking action to prevent and treat gum disease is essential for maintaining healthy gums and teeth. By understanding the causes and risk factors, individuals can make informed decisions and take the necessary steps to protect their oral health.